Domain names are a crucial element of the internet.
If your website is a house, then your domain name is its address.
The giant network of computers that connect to each other via the internet are identified by an IP address. IP addresses are made up of numbers and are rather difficult to remember. Domain names solve this problem so that instead of having to enter a long string of unmemorable numbers, we can simply type in the name of our favourite brand into the browser address bar.
Which would you rather have to remember? 216.58.212.206 or www.google.com?
It makes using the internet so much easier - the Domain Name System (DNS) synchronises the domain name with the IP address and you’re sent the site files which allow you to view the website in question.
There are currently more than 1,500 domain name extensions available for use and currently 363.5 million domain names registered across all top-level domains (TLDs).
The first ever registration of a .com domain was in 1985. It was registered by the computer company Symbolics Inc. based in Massachusetts, USA. Over the years, ownership of the domain has changed hands and it is now an online museum about the internet and the world wide web.
These are the first 10 registered domain names:
- March 15, 1985 - symbolics.com
- April 24, 1985 - bbn.com
- May 24, 1985 - think.com
- July 11, 1985 - mcc.com
- September 30, 1985 - dec.com
- November 7, 1985 - northrop.com
- January 9, 1986 - xerox.com
- January 17, 1986 - sri.com
- March 3, 1986 - hp.com
- March 5, 1986 - bellcore.com
Domains under .com are the most registered domains worldwide.
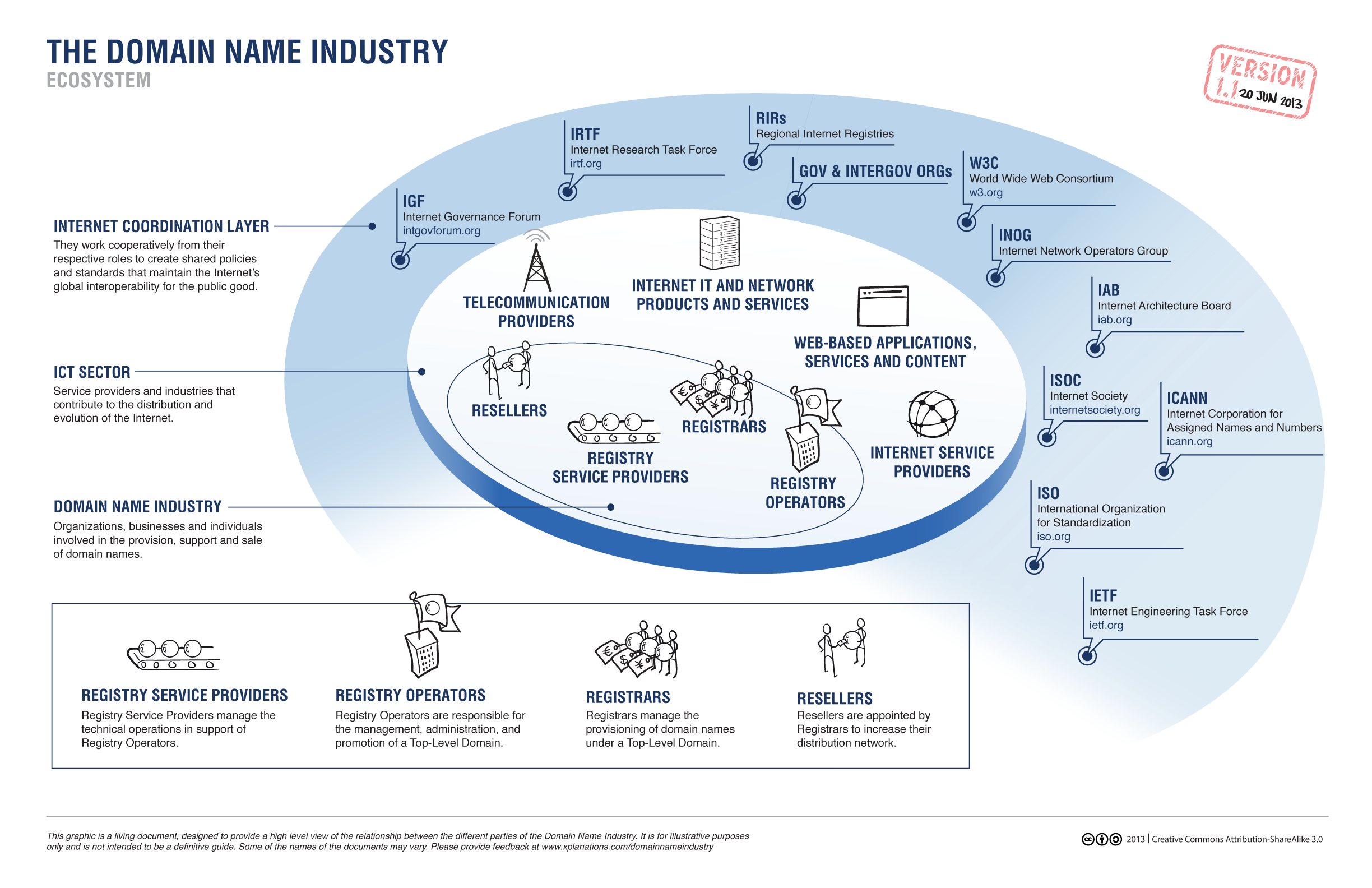
The key players in the industry
REGISTRY OPERATOR: A domain name registry is the technical operator and manager of a TLD domains and subdomains. They almost exclusively work with registrars to sell their domain names to the public. Most registry operators outsource the critical technical infrastructure of their TLD(s) to a REGISTRY SERVICE PROVIDER such as CentralNic.
REGISTRAR: Registrars are used to register a domain. They sit between the registrant and the registry operator and work with registries to acquire domain names for individuals and companies.
REGISTRANT:The registrant is the person or company that is the registered holder and owner of a domain. They hold the rights to the domain for a defined period of time, although the registration can be renewed indefinitely. If the registrant makes changes to the domain, the registrar will pass on that information to the registry, which then updates its database.
This graphic from ICANN neatly shows what the wider domain name industry looks like and the relationships between all the players.